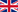
Cobitidae
Cobitidae, or True loaches (popular name a Pinch or a Spike) is rare inhabitant of a home aquarium. It is quite unpretentious, and very exciting schooling fish.
 Cobitis paludica. Photo from: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cobitis_paludica
Cobitis paludica. Photo from: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cobitis_paludica
Despite some similarities with the loach, this fish differs, both in habits and in conditions of detention. Cobitis are much more demanding on water quality, impurities and oxygen. In addition, cobitis have thorns with which they can injure the aggressor (hence the popular name of the fish). The pinch thorns are used only in case of an unexpected attack on them. They themselves do not attack and lead a peaceful life.
About Cobitis in general
Aquarium keeping
* Water * Lighting *
* Soil * Equipment*
* Feeding *
Compatibility with other fish
Attitude to plants
Breeding in aquarium
Species of cobitis
* Taenia * Choi *
* Bilineata * Bulgarica *
* Lutheri * Macrostigma *
* Minamori * Sabanejewia Aurata *
* Pumila * OTHER KIND *
Briefly about the main
Keeping conditions
Temperature: 5 - 25 C. Acidity: 6.0-8.0; pH.
Water hardness: 4 - 21 gH. Adult size: up to 6 - 14 cm.
Habits: peaceful, gregarious. Feeding: omnivores.
Minimum volume for a couple: from 50 liters.
Lifestyle: data.
Use in the aquarium: they eat leftover food, small snails.
Attitude to plants: indifferent.
According to science
СFamily: Cobitidae.
Genus: Cobitis. Type: Multiple.
In Latin: Cobitis taenia.
Cobitis, like many other fish, even being caught from a natural reservoir, quickly enough adapts to the condition of the aquarium. This fish is unpretentious, the light and the relatively warm water of the aquarium is acceptable.
About Cobitis in general
Cobitis belongs to the Loach family and is found in freshwater throughout Europe. Unlike the loach, which can live in any swamp, the spiny loach prefers cleaner bodies of water. The bottom of the reservoir should be covered with silt, and more often with sand or large stones, where the fish is hiding from predators.
They are the smallest fishes in the loach family. Adults length rarely reaches 12 cm with elongated body and flattened on the sides. The head is small, with a slightly upturned nose. The mouth is directed downward, around it there are 6 sensitive antennae of different lengths. The eyes are small, yellow, located in the frontal part. Under the eyes (on the gill covers) there are sharp spines, which. In case of danger, these spines leave their cavity and, issuing a characteristic click, bulge out. Hence the name a pinch or a spike.
The fins are small, transparent, almost colorless or decorated with dark spots. The main body color is gray-brown with two rows of round dark spots. The abdomen is lighter, yellowish, the scales are small.
In the reservoirs of central Russia, the number of Shchipovka is decreasing, which is associated with both the spread of invasive Chinese sleeper (Rotan), erosion of the banks by water transport, and the "improvement of embankments" - the construction of embankments or recreation sites.

Cobitis delicata. Фото с сайта: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cobitis
Keeping a Cobitis in an aquarium
Cobitis unpretentious and does not require special conditions or complex care. This fish is slightly more demanding on water quality, oxygen content and pollution than Loach.
Water
The spiker prefers to live in clean water, so a good filter and aerator should be. The presence of a thermostat is not necessary, since the fish feels good in cool water. Optimum water parameters: temperature + 17- + 24oC, pH 7.0-7.7, dGH 10-250. Changes are made weekly, about 20-25% of the total volume of the tank.
Lighting
These fishes tolerate both bright light and shade very well. But, when using bright lamps, their color quickly become lighter, in shade the fish darkens.
Aquarium soil
It is advisable to use sand (then it will be funny to watch how smartly the pinch burrows into it). You can use any shallow aquarium substrate. Due to the fact that Cobitis like to dig in the ground, it is better to press the plants with stones or plant them in pots. Also, this fish like pebble soils if there are plases to hide.
Aquarium and equipment
Cobitis feels comfortable in a small company of relatives. For 3-4 fish, the volume of the tank should be at least 50 liters. The aquarium should have a lid so that the fish cannot jump out. It is necessary to create shaded areas with plants, grottoes and shelters. Small pebbles or sand are poured at the bottom.
Feeding
In nature, Spike finds food for itself, mostly at the bottom. It can be as various crustaceans, larvae, small snails, and plant debris, drowned insects or scraps of other fish. When keeping in the aquarium, the Spike will collect from the bottom whatever remains after feeding other fish. Both dry food and various ground meat and live food are excellent. The key to the health of any fish, not only Cobitises, is a variety of food! Food can also be given in the evening or after turning off the lights, when the Pinchers are even more active. Sometimes you can pamper Pinchworm with bloodworms and brine shrimp.
Despite the fact that these are bottom fish, they can easily take food from the surface. In any case, their closest relatives, the Loaches, eat well from the surface.
Compatibility with other fish
With fish and other inhabitants
Cobities prefer to live in small flocks of 3-5 individuals (alone they become shy and nervous). These fish swim mainly in the lower tier of the reservoir. In evening their activity increased.
Cobitises can completely bury themselves in the sand in case of danger and, as mentioned above, hit the attacker with sharp spikes. Despite such aggressive defense mechanisms, Pinches are peaceful neighbors and never initiate agression with their neighbors. They easily get along with many fish, which can live with them in the same temperature regime: goldfish, cardinals, pseudo-skates, cyprinidae, mollies and many many others. Large and aggressive fish, as well as species with obvious territorial inclinations, will be unwanted neighbors for Cobities. Also, conflicts for shelters with other bottom ones are possible, but this is possible only in small aquariums and with a lack of nooks and crannies.
Cobitises are omnivorous, and everything that fits into the mouth will be eaten (caviar, small snails, fry).
Attitude to plants
Plants are treated indifferently. If in the aquarium it is desirable to strengthen the sandy soil of the plants with pebbles (or plant in a pot). Almost any plants can be used: anubias, cryptocorynes, hygrophils, hornworts, which will form thickets in the corners and at the back of the aquarium. Floating plants such as nayas, elodea, nymphea, eichhornia, duckweed, wolfia and other species are also great.
Breeding of Cobitidae in the aquarium
The spikes reach maturity by 2-3 years. Males differ slightly from females: females are larger, and males have larger fins and a small bony plate on the elongated ray of the pectoral fin.
To prepare the fish for spawning, the female and the male are placed in different tanks towards the end of winter. For guaranteed reproduction, during separation, it is advisable to gradually lower the temperature to 10 C and even lower, but this is not necessary.
In late May - early June, fish are united in a spawning aquarium. Shortly before combining, the fish begin to feed with live food and feed the entire spawning period. Water should be fresh and clean, temperature +26 - +28 С, pH 6.0-7.0, hardness 6.0-9.00dGH.
In 2-3 weeks female and the male, one can observe mating dances and an increase in the abdomen of the female.
The spawning aquarium can be small, about 15-20 liters. When decorating, it is enough to use several stones, which are laid out along the edges and covered with Javanese moss (this is important, since fish moss is used as a place for laying eggs). Filter with weak flow will be good. It is also necessary to equip the spawning aqua with lamps; for several days of maximum activity, the light should be on around the clock.
Spawning lasts 2-5 days. The average productivity of a female is about 300 eggs. During fertilization, fish are very active. As soon as they lie on the bottom of the aquarium and calm down, they can be returned to the general aquarium.
Eggs are small, flattened, 1-3 mm in size. Caviar ripens in 4-6 days, after which small larvae begin to appear, which bear little resemblance to future fish. For the first 3 days, they feed on the yolk sac and lie at the bottom of the aquarium or attach to plants. On the fourth day, they become more like fish. They develop external gills and eyes. Fry at this age are able to independently seek food for themselves. At this time, they are fed with special food for fry, microworms and enchitrea, at this time water changes must be started. Young small fish grow quickly and after 2 weeks they grow up to 1 cm in size. As the fish grow, they are transferred to more adult food. After one year they are transported into a comfortable aquarium with soil, plants, driftwood and decorations.
Types of Cobitidae
The genus of Cobitidae includes many species, all of them are very similar to each other, both in appearance and in habits. It is difficult even for a professional to distinguish one species from another. Most of the species are presented below:
Cobitis taenia
is actually the hero of the article.
Cobitis choii
A poorly studied species, characterized by a yellowish tinge. The back is yellow-brown, the abdomen is light yellow. Row of rounded brown spots on the sides. A black spot at the base of the caudal fin. Occurs in Korea, Mongolia, North-East China, Far East of Russia (Amur river). Size up to 8 cm.
Cobitis bilineata
Has 2 rows of dark spots (almost transient in the line). There are two black spots at the base of the tail. Tail straight. Dorsal and caudal fins with small specks. Habitat: eastern, central Europe (Croatia, northern Italy, Switzerland). Size up to 7 cm.
Sabanejewia bulgarica
Yellowish brown or gray-brown fish with large spots. There is a black line at the base of the caudal fin. A blurred black stripe from the eyes about the mouth. Habitat: Danube basin. Size up to 12 cm.
Cobitis lutheri
It has a light yellow body with brown spots, 2 black stripes on the head (one runs along the gills, the other through the eye). 2 spots at the base of the caudal fin upper black in the shape of a crescent, lower one barely noticeable. Habitat: Korea Peninsula, northern China, Amur basin, Sakhalin. Size 8 - 12 cm.
Cobitis macrostigma
The body is light gray, large brown spots, blurred along the edges, has an elongated body. Habitat: China (Yangtze River). It grows up to 13 - 14 cm.
Cobitis minamorii
The body is light brown, on the sides along the body there are 2 stripes (rarely intermittent): dark brown in the middle, lighter above, 2 dark spots at the base of the tail in the shape of a crescent. Habitat: fresh water bodies of Japan. It grows up to 6 - 7 cm.
Sabanejewia aurata
The body is golden, but with a lot of dark spots, which makes the fish look darker. Depending on the habitat, it may differ in appearance. Habitat: Don, Danube, Kuban, found in the rivers of the Caucasus, Central Asia. Size: up to 14 cm.
Cobitis Pumila
Light brown to yellow-brown body with distinct brown spots. The head is covered with small black specks. Habitat: Southwest Korea, Kumgan River. Grows up to 7 cm.
And there are also: Chipovka Cetinskaya, Chipovka Shikoku, Chipovka Biwa, Chipovka Danube, Chipovka Iberian, Chinese, Korean ...
Cobitis, despite the lack of bright colors, are very interesting and attractive fish. They, like many Loaches, are able to respond to changes in atmospheric pressure, and are a kind of "living barometers". Observing their behavior is very exciting, especially when they are "screwed" into the ground with their tail, leaving only the head or the front of the body in sight. It is not at all difficult to keep and grow them, while they will delight every day with their energy and unusual appearance.